Tornado Cash Sanctions Expose Potential DeFi Achilles’ Heel
The US blacklisted dozens of Ethereum addresses when it sanctioned Tornado Cash. Can a major DeFi protocol like MakerDAO get caught in the dragnet?
Source: DALL·E
- Stablecoin issuer Circle quickly followed the US Treasury in blacklisting dozens of USDC addresses over ties to Tornado Cash
- MakerDAO’s DAI is currently backed by more than 32% USDC, raising concerns about its influence on the stablecoin
The US Treasury has sent blockchain protocols scrambling to identify potential exposure to sanctioned crypto mixer Tornado Cash — with some suggesting MakerDAO must act quickly to protect its stablecoin.
Authorities officially sanctioned Ethereum-powered Tornado Cash on Monday by adding its blockchain addresses to the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) blacklist, effectively rendering it illegal for any US person to interact with the app.
Tornado Cash, which runs on immutable smart contracts, commingles cryptoassets from many individuals to hide the funds’ provenance. It’s a privacy tool with many legal and beneficial uses, such as donating to politically-charged causes privately, or preventing casual financial surveillance.
Lawful users can prove the origin of funds coming from Tornado Cash using a cryptographic note — a kind of receipt — when required to do so by a legal authority.
But authorities allege it’s a popular method of laundering stolen crypto among North Korean hackers, who’ve been tied to a number of token bridge hacks, including the Axie Infinity and Nomad incidents.
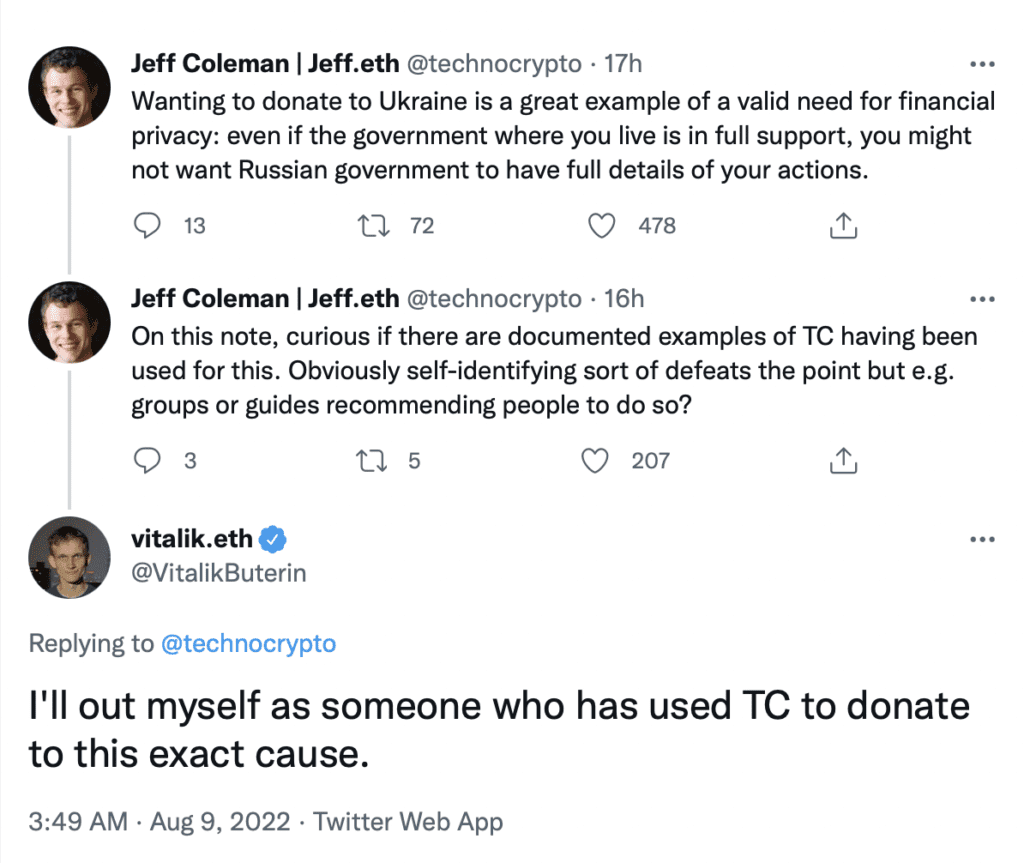
Shortly after the US Treasury’s latest sanctions against Tornado Cash came to light, stablecoin issuer Circle began blacklisting the 45 Ethereum addresses named by OFAC.
OFAC’s list contains addresses directly associated with Tornado Cash, such as its various pools for mixing cryptocurrency. It also cites a Tornado Cash address utilized by crypto grants program Gitcoin to field donations — the biggest of which came from the hacker behind the $37.5 million Iron Bank exploit last February.
Addition to the OFAC list makes it impossible for address owners to send or receive USDC. The move is not unprecedented; practically all centralized stablecoin issuers — including Circle and Tether — have censored bad actors in the past.
Not to mention, major Ethereum infrastructure provider Infura dropped Tornado Cash as a client overnight. “Our understanding is that they [Tornado Cash] used Infura to support Ethereum calls made by their front-end user interface,” Bill Hughes, director of global regulatory matters at ConsenSys, told Blockworks in an email.
But Circle’s round of blacklist additions is viewed by some as an act of censorship at the behest of a US government agency: a big no-no among parts of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
MakerDAO stability mechanism relies on USDC
MakerDAO governs arguably the ecosystem’s most decentralized stablecoin offering, DAI. It’s the fourth-largest stablecoin, commanding $7 billion in circulating supply.
DAI is novel in that MakerDAO stakeholders decide almost everything about the token: its asset backing, issuance and interest rates, staffing, investment allocation and supporting budgets.
This contrasts how Tether and Circle, the two largest stablecoin issuers, operate. They’re both centralized, private companies and decide critical decisions behind closed doors, with practically no on-chain accountability sans basic supply stats and simple attestations to their backing. More than $120 billion in USDC and USDT circulate around the cryptocurrency industry.
With this in mind, MakerDAO potentially faces an existential problem. The protocol — which markets itself as an “unbiased” and “decentralized” stablecoin usable by anyone, anywhere — has grown reliant on USDC to maintain its peg to the dollar. Half of all DAI was initially generated from USDC deposits, while MakerDAO is currently backing its stablecoin’s by about one-third USDC.
MakerDAO benefitted from USDC, which is quite stable, throughout the year’s market chaos, a period marked by the stablecoin-equivalent of bank runs on USDT.
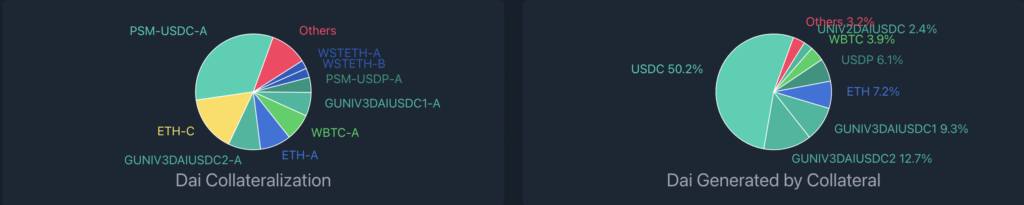 Source: Daistats.com
Source: Daistats.com
But the protocol’s exposure to USDC goes deeper than just a centralized treasury. In an interview with Blockworks, MakerDAO delegate and crypto researcher Mika Honkasalo detailed what’s known as the Price Stability Module (PSM), which could have just become a target for anyone looking to profit from DAI’s depegging.
As the name suggests, PSM helps keep the price of DAI pegged to the US dollar, particularly when demand outstrips supply. DAI is issued only when overcollateralized deposits are made to the protocol — if lots of people want DAI tokens, but there’s little by way of collateral, a supply crunch could skyrocket the price of DAI beyond its intended $1.
PSM was MakerDAO’s solution: Allow USDC holders to swap their tokens for “expensive” DAI at the dollar rate. It presents an immediate and potentially lucrative arbitrage opportunity at times when DAI’s price spikes beyond one dollar, which should inspire the price of DAI to match USDC.
Anyone at all can send USDC to MakerDAO’s PSM, at which point the tokens are technically controlled by MakerDAO.
This has sent alarm bells ringing for Honkasalo.
A brand-new attack vector with little downside
A bad actor could view the Treasury’s Tornado Cash dragnet, which has already caught bystander donors via Gitcoin, as the blueprint for a brand-new attack vector: sending USDC to sanctioned Tornado Cash, thereby tainting it, before forwarding it to MakerDAO — a guilt-by-association “dust attack.”
If that specific USDC ever happens to be on the sanctions list, the value of that USDC is theoretically zero, which means MakerDAO would lose a lot of its collateral,” Honkasalo said.
Hypothetically, an attacker who believed the FBI, say, to be supremely adversarial with the cryptocurrency ecosystem could open a DAI short at the same time, and wait for the US Treasury to potentially sanction MakerDAO’s stability peg for its “interaction” with Tornado Cash, which would undermine its backing and, critically, its price.
Holders of Maker’s MKR token are ultimately responsible for DAI’s stability, and in this unlikely scenario, the protocol would mint and sell MKR as a last resort, destroying its market cap as well.

“Of course, you’re not guaranteed to get on the sanctions list,” Honkasalo said. “But, depending on the process of how that’s chosen, you could, so it’s probably an EV-positive [expected value positive] bet.”
Honkasalo prescribed the protocol to diversify away from USDC and into tangible, real-world assets such as US Treasurys and bonds, however those processes take time.
There’s a kicker: MakerDAO is not the only protocol susceptible to these kinds of attacks, according to Honkasalo. This is potentially an issue for every single DeFi protocol that has USDC assets as collateral.
Frax, the protocol behind the semi-algorithmic stablecoin of the same name, similarly relies on USDC inflows — with its treasury historically made up of more than 90% USDC, although the platform says it keeps only a small portion of it in addresses vulnerable to OFAC sanctions.
“All the lending markets actually suffer from this equally, people have just realized that DAI has a problem, but the auto-lending markets are just as much backed by USDC as DAI,” Honkasalo said.
“The real problem is worse because it’s across all of the different protocols that have USDC.”
Jerry Brito, executive director at blockchain research group Coin Center, however, threw cold water on the idea that the US Treasury would freely hand out sanctions to any address interacting with Tornado Cash moving forward.
“I would think that’s unlikely, and I’d be surprised if this would metastasize that quickly in those directions,” Brito told Blockworks. “It seems, from their previous statements, they are very specifically concerned about mixers, particularly those used by specific bad actors — North Korean hackers and ransomware attackers.”
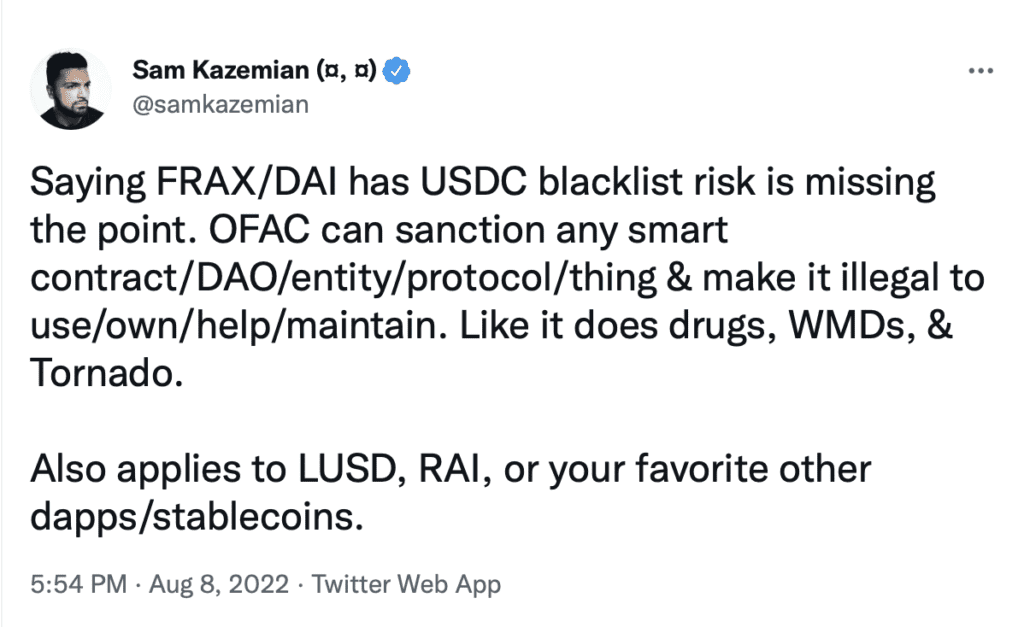
For what it’s worth, Frax founder Sam Kazemian addressed the risks posed by USDC in a Telegram chat on Monday, saying: “Fiatcoins could indeed blacklist all of Curve/Uniswap/Aave contracts with no warning, technically, but keep in mind that would also destroy USDC to zero overnight.”
Indeed, a doomsday scenario involving Circle taking its US allegiance to the extreme, blacklisting anyone for interacting with Tornado Cash, seems unrealistic.
But Infura and Circle’s immediate adherence to OFAC’s sanction has exposed centralization vulnerabilities across DeFi, many of which may be unnoticed at this time.
This article was updated at 1:27 pm ET, August 11 to correct the amount of USDC backing DAI’s supply.
Get the news in your inbox. Explore Blockworks newsletters:
- The Breakdown: Decoding crypto and the markets. Daily.
- 0xResearch: Alpha in your inbox. Think like an analyst.






